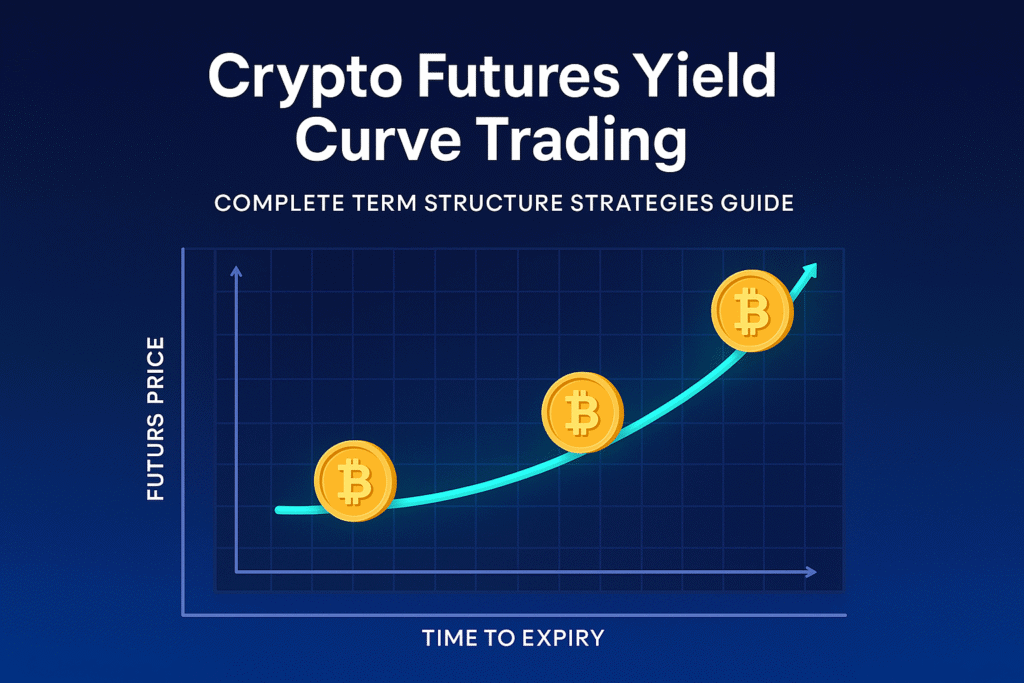
Crypto futures yield curve trading represents one of the most sophisticated yet underutilized strategies in digital asset markets. While traditional bond traders have used yield curve analysis for decades, crypto traders are only beginning to discover the powerful signals hidden in futures term structures and the profitable opportunities they create.
Most crypto traders focus exclusively on spot price movements while completely ignoring the valuable information embedded in futures curves. This oversight misses critical market intelligence about supply, demand, sentiment, and institutional positioning that can provide significant trading advantages in volatile crypto markets.
The relationship between different expiration dates in crypto futures reveals market expectations, carrying costs, and the balance between short-term speculation and long-term investment flows. Understanding these dynamics enables traders to position ahead of major moves and profit from structural inefficiencies that others overlook.
New to the platform? Our Bitunix trading tutorial walks you through every step.
If you’re starting small, read how one trader went from $500 to $5,000 with a crypto futures strategy.
This complete guide explores crypto futures yield curve fundamentals, practical trading strategies, and advanced term structure analysis techniques. Whether managing institutional portfolios or sophisticated individual accounts, these concepts provide essential tools for handling complex crypto derivatives markets with greater precision and profitability.
Crypto Futures Yield Curve Analysis Framework
Understanding crypto futures term structures requires analyzing the relationship between contracts with different expiration dates. Unlike traditional commodities with physical storage costs, crypto futures curves primarily reflect market sentiment, use demand, and institutional positioning rather than carrying costs.
Bitcoin Futures Curve Patterns
Bitcoin futures typically trade in mild contango during normal market conditions, with longer-dated contracts priced slightly above near-term contracts. This reflects the general expectation of price appreciation over time, combined with the premium investors pay for future delivery without immediate capital commitment.
Extreme contango situations develop during bull markets when leveraged long demand exceeds available futures supply. These conditions often signal speculative excess and potential market tops, creating high-probability short opportunities for experienced traders.
Backwardation in Bitcoin futures remains relatively rare but provides powerful reversal signals when it occurs. These conditions typically develop during severe market stress when spot demand significantly exceeds futures interest, often marking major market bottoms.
Crypto Futures Term Structure Trading Strategies
| Strategy Type | Market Condition | Implementation | Risk Level | Typical Duration |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Curve Steepening | Bull market acceleration | Long distant, short near | Medium | 2-8 weeks |
| Curve Flattening | Market maturation | Short distant, long near | Medium | 3-12 weeks |
| Roll Yield Capture | Persistent contango | Calendar spread rolling | Low-Medium | Ongoing |
| Backwardation Play | Market capitulation | Long futures, short spot | High | Days to weeks |
| Butterfly Spread | Curve distortion | Multi-leg positioning | Medium-High | 2-6 weeks |
Curve Steepening Strategies
Curve steepening trades profit from situations where longer-dated futures premiums increase faster than near-term premiums. This typically occurs during the early stages of bull markets when institutional investors begin accumulating longer-term positions while short-term traders remain cautious.
The most straightforward steepening trade involves buying longer-dated futures contracts while simultaneously selling near-term contracts. This spread position profits as the curve steepens, regardless of overall price direction, providing some downside protection during volatile periods.
Advanced steepening strategies incorporate multiple expiration dates to create more precise exposure to specific parts of the curve. These butterfly-type structures can capture curve changes while minimizing overall directional risk through careful position sizing and hedging.
Curve Flattening Opportunities
Curve flattening represents the opposite scenario, where near-term and longer-term futures premiums converge. This often occurs during late-stage bull markets when speculative excess pushes near-term contracts to extreme premiums while longer-term positioning becomes more cautious.
Successful flattening trades require careful timing since extreme contango conditions can persist longer than expected. Using graduated entry strategies and proper risk management helps handle the timing challenges inherent in these high-conviction trades.
Platform selection becomes important for executing complex term structure strategies. Bitunix provides advanced futures curve analysis tools with real-time term structure data and integrated spread trading capabilities that serious yield curve traders require for consistent execution and profitability.
Roll Yield and Calendar Spread Mechanics
Roll yield represents one of the most consistent profit opportunities in crypto futures markets, particularly during persistent contango conditions. This strategy involves systematically capturing the premium decay as futures contracts approach expiration and converge toward spot prices.
Understanding Roll Yield Dynamics
When Bitcoin or Ethereum futures trade in contango, the premium between futures and spot prices represents potential profit that can be captured through careful position management. As contracts approach expiration, this premium naturally decays, creating predictable profit opportunities for patient traders.
The magnitude of roll yield depends on the steepness of the futures curve and the time remaining until expiration. Steeper curves provide higher potential returns but also indicate greater market risk, requiring more sophisticated risk management approaches.
Professional traders often combine roll yield strategies with directional views to improve returns. During bullish periods, maintaining net long exposure while capturing roll yield provides both directional profits and structural premium capture.
Calendar Spread Implementation
Calendar spreads form the foundation of most yield curve trading strategies, involving simultaneous long and short positions in different contract months. These trades isolate curve shape changes from overall price movements, providing more stable return profiles during volatile periods.
Effective calendar spread trading requires understanding proper risk management techniques specific to multi-leg derivatives strategies. Position sizing, correlation analysis, and dynamic hedging become essential skills for managing complex spread portfolios.
The selection of contract months significantly impacts spread performance. Generally, trading between consecutive months provides tighter spreads but smaller profit potential, while trading between quarterly contracts offers higher potential returns with increased risk and volatility.
Advanced Term Structure Analysis
Professional crypto futures traders analyze term structures across multiple dimensions to identify trading opportunities and manage portfolio risk. This multi-faceted approach considers time decay, volatility expectations, and institutional flow patterns simultaneously.
Cross-Asset Curve Analysis
Comparing Bitcoin and Ethereum futures curves reveals relative strength and weakness between major crypto assets. Divergences often signal pair trading opportunities or broader market regime changes that affect portfolio allocation decisions.
When both Bitcoin and Ethereum show similar curve patterns, it typically indicates broad-based sentiment shifts affecting the entire crypto market. Conversely, divergent patterns may suggest asset-specific factors creating relative value opportunities.
Advanced traders also monitor correlations between crypto futures curves and traditional financial markets. During periods of high correlation, crypto curves may respond to bond market movements, creating additional analytical dimensions for strategy development.
Institutional Flow Analysis
Large institutional trades often create temporary distortions in futures curves that provide trading opportunities for nimble participants. Understanding typical institutional trading patterns helps identify when curve shapes reflect temporary flow imbalances rather than fundamental value.
Quarterly contract expirations frequently create predictable institutional rebalancing flows that affect curve shapes. Traders who understand these patterns can position ahead of expected flows to capture profits from temporary dislocations.
The growth of crypto ETFs and structured products has introduced new institutional flow patterns that affect futures curves. Monitoring these developments helps traders adapt strategies to evolving market structure changes.
Risk Management for Curve Trading
Crypto futures yield curve trading involves unique risks that require specialized management approaches beyond traditional futures trading techniques. Understanding these risks and implementing appropriate controls determines long-term strategy success.
Correlation Risk Management
Multi-leg strategies expose traders to correlation risk when the relationships between different contract months change unexpectedly. During extreme market stress, correlations often break down, creating losses even in theoretically hedged positions.
Dynamic hedging approaches help manage correlation risk by adjusting position ratios as market conditions change. This requires continuous monitoring and sophisticated execution capabilities that separate professional from amateur curve traders.
Platform capabilities become essential for managing complex correlation exposures. Understanding which exchanges provide superior risk management tools helps ensure that theoretical strategies translate into practical profitability.
Liquidity Considerations
Crypto futures liquidity varies significantly across different contract months, with near-term contracts typically offering the tightest spreads and deepest order books. This liquidity differential affects execution quality and position management flexibility.
Traders must carefully consider liquidity when sizing positions and planning exit strategies. Holding large positions in illiquid contract months can create significant execution risk during volatile periods when quick position adjustments become necessary.
Building relationships with professional market makers and understanding institutional trading patterns helps navigate liquidity challenges in longer-dated contracts where retail participation remains limited.
Technology and Platform Requirements
Successful crypto futures yield curve trading demands sophisticated technology infrastructure beyond basic futures trading platforms. Real-time curve analysis, multi-leg order execution, and complete risk monitoring become essential operational requirements.
Essential Platform Features
Effective curve trading requires platforms with integrated spread trading capabilities, real-time term structure visualization, and advanced order management systems. These features distinguish professional-grade platforms from basic retail offerings.
| Platform Feature | Importance Level | Professional Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Real-time curve data | Critical | Accurate spread pricing |
| Multi-leg execution | Critical | Simultaneous order fills |
| Risk analytics | High | Portfolio exposure monitoring |
| Historical curve data | High | Strategy backtesting |
| API connectivity | Medium | Automated execution |
Bitunix’s institutional-grade platform provides complete yield curve trading tools including real-time term structure analysis, integrated spread execution, and sophisticated risk management capabilities that retail platforms typically lack.
Data and Analysis Requirements

complete historical data becomes essential for developing and testing curve trading strategies. Understanding how curves behaved during different market regimes helps traders calibrate position sizing and risk management parameters.
Real-time data feeds must include not just prices but also volume, open interest, and institutional flow indicators that affect curve dynamics. This complete market intelligence enables more informed trading decisions and better risk management.
Market Regime Analysis
Crypto futures curves behave differently across various market regimes, requiring adaptive strategies that adjust to changing conditions. Understanding these regime differences helps traders optimize strategy selection and position sizing for current market environments.
Bull Market Curve Characteristics
During sustained bull markets, crypto futures curves typically steepen as longer-term optimism exceeds near-term caution. This creates persistent roll yield opportunities for systematic strategies while providing directional profits for properly positioned traders.
Bull market curves often exhibit increasing volatility as speculative activity intensifies. This volatility creates both opportunities and risks that require careful management through position sizing and dynamic hedging approaches.
The late stages of bull markets frequently show extreme contango conditions that provide high-probability reversal signals for experienced traders. Recognizing these conditions helps avoid major drawdowns while positioning for trend changes.
Bear Market Dynamics
Bear markets typically flatten or invert crypto futures curves as near-term selling pressure exceeds longer-term accumulation interest. These conditions create different trading opportunities that require modified strategies and risk management approaches.
Backwardation conditions during bear markets often provide excellent long-term buying opportunities but require significant patience and risk tolerance. The timing of these trades becomes important since further declines can persist longer than expected.
Bear market curve trading often involves more defensive strategies focused on capital preservation rather than aggressive profit seeking. Understanding this shift helps traders maintain appropriate risk levels during challenging periods.
Institutional Applications
Professional crypto traders and institutional investors increasingly use yield curve analysis for portfolio management, risk control, and alpha generation. These applications demonstrate the practical value of curve trading beyond pure speculation.
Portfolio Hedging Strategies
Large crypto holders use futures curves to hedge portfolio exposure while maintaining upside participation. Understanding curve dynamics helps optimize hedge ratios and minimize costs while preserving desired risk exposures.
Institutional hedging often involves complex multi-leg strategies that require sophisticated execution and risk management capabilities. Working with platforms that understand institutional requirements becomes essential for implementing these strategies effectively.
Alpha Generation Techniques
Systematic curve trading strategies provide consistent alpha generation opportunities for institutional portfolios. These strategies typically focus on capturing structural inefficiencies rather than directional market moves.
Quantitative approaches to curve trading involve statistical analysis of historical patterns, mean reversion strategies, and momentum-based systems. Implementing these approaches requires solid data infrastructure and sophisticated risk management systems.
Expert Insight from Lucas Tran
Lucas Tran, Cryptocurrency Researcher & Market Analyst
After seven years of analyzing crypto derivatives markets, I’ve found that yield curve trading represents one of the most underexploited opportunities in digital assets. The sophistication gap between traditional fixed income and crypto futures creates persistent inefficiencies that informed traders can systematically capture.
My most successful curve trades have involved identifying extreme contango conditions during bull market peaks and positioning for curve flattening through calendar spreads. The 2021 bull market provided several months of profitable curve flattening opportunities as retail speculation pushed near-term contracts to unsustainable premiums while institutional positioning remained more measured in longer-dated contracts.
The key insight that transformed my approach was understanding that crypto futures curves reflect sentiment and positioning more than fundamental carrying costs. Unlike commodity futures where storage and financing create natural curve shapes, crypto curves are purely psychological constructs that can reach extreme levels before reverting.
Risk management becomes absolutely critical in curve trading because these strategies can experience extended periods of adverse performance before ultimately proving profitable. I typically limit individual curve trades to 1-2% of capital and use scaling entries to manage timing risk. The ability to hold positions through temporary adverse moves often determines strategy success.
Platform selection has proven important for consistent execution. I’ve primarily used Bitunix for curve trading because their integrated spread tools and real-time term structure analysis provide significant operational advantages. The ability to execute complex multi-leg trades simultaneously while monitoring real-time curve changes has improved my execution quality substantially.
Looking forward, I expect institutional adoption to reduce the magnitude of curve extremes but create new opportunities in relative value trading between different crypto assets. The key will be adapting position sizes and expectations while maintaining focus on the fundamental drivers of curve behavior in evolving market structures.
Implementation Framework
Developing systematic approaches to crypto futures yield curve trading requires structured frameworks that combine market analysis, strategy selection, and risk management into coherent trading systems.
Strategy Development Process
Successful curve trading begins with complete historical analysis to understand typical curve behaviors across different market conditions. This foundation enables traders to develop realistic expectations and calibrate appropriate position sizing for various strategies.
Backtesting curve strategies requires careful attention to execution assumptions, transaction costs, and liquidity constraints that may not be apparent in theoretical analysis. Real-world implementation often differs significantly from idealized backtests.
Position Management Protocols
Systematic position management becomes essential for curve trading success since these strategies often involve multiple contracts with different risk characteristics. Clear rules for position sizing, scaling, and exit criteria help maintain discipline during challenging periods.
Correlation monitoring helps identify when strategy assumptions break down and position adjustments become necessary. This dynamic approach to risk management separates successful curve traders from those who rely on static position management.
Market Structure Evolution
The crypto futures market continues evolving rapidly, with new products, participants, and trading patterns affecting curve dynamics. Understanding these changes helps traders adapt strategies to maintain effectiveness in changing market structures.
New Product Impacts
The introduction of micro futures contracts, options on futures, and ETF creation/redemption mechanisms affects underlying futures curves in complex ways. Traders must monitor these structural changes and adapt strategies accordingly.
Regulatory developments also influence curve shapes as institutional participation patterns change. Understanding regulatory impacts helps anticipate structural shifts that affect long-term strategy viability.
Technology Developments
Advancing trading technology enables more sophisticated curve analysis and execution capabilities. Staying current with technological developments helps traders maintain competitive advantages in rapidly evolving markets.
Artificial intelligence and machine learning applications increasingly influence curve trading, creating both opportunities and challenges for traditional analytical approaches. Adapting to these technological changes becomes essential for long-term success.
Frequently Asked Questions
What makes crypto futures yield curves different from traditional markets? Crypto futures curves primarily reflect sentiment and leverage demand rather than physical carrying costs, making them more volatile and prone to extreme conditions than traditional commodity or bond curves.
How much capital is needed to trade crypto futures curves effectively? While theoretical minimum amounts vary, practical curve trading typically requires $50,000+ to properly diversify across multiple strategies and manage correlation risks effectively.
Which crypto futures show the most reliable curve patterns? Bitcoin and Ethereum futures provide the most liquid and predictable curve patterns due to higher institutional participation and trading volumes compared to smaller altcoin futures.
How do I identify extreme curve conditions? Extreme contango typically involves premiums exceeding 15-20% annualized, while backwardation of any magnitude in crypto futures usually signals extreme conditions requiring attention.
Can curve trading be automated? Basic curve monitoring can be automated, but successful trading requires discretionary analysis of market context, institutional flows, and regime changes that automated systems struggle to interpret.
How do funding rates relate to futures curves? Perpetual swap funding rates often correlate with futures curve steepness, providing additional confirmation signals for curve-based trading strategies.
What’s the typical holding period for curve trades? Most curve trades require 2-12 week holding periods to allow time for curve normalization, though extreme conditions may resolve more quickly during volatile periods.
How do I manage correlation risk in multi-leg strategies? Dynamic hedging, position scaling, and continuous correlation monitoring help manage the risk that different contract months may not move as expected relative to each other.
Should beginners attempt yield curve trading? Curve trading requires solid understanding of futures markets, derivatives risk management, and institutional trading patterns. Beginning traders should master basic futures trading first.
How do macro events affect crypto futures curves? Major regulatory announcements, institutional adoption news, and traditional market stress can rapidly reshape crypto futures curves, requiring fundamental analysis alongside technical curve analysis.
Which platforms provide the best curve trading tools? Professional curve trading requires integrated spread execution, real-time term structure data, and sophisticated risk management capabilities that distinguish institutional platforms from retail offerings.
Can I trade curves with small position sizes? While possible, small positions may not justify the complexity and monitoring requirements of curve trading strategies. Focus on highest-conviction opportunities when working with limited capital.
How do options expirations affect futures curves? Large options expirations can create temporary curve distortions as institutional hedging flows impact futures markets, creating short-term trading opportunities for aware participants.
What role does open interest play in curve analysis? Open interest patterns across different contract months reveal institutional positioning and potential flow directions that can help predict curve movements and identify trading opportunities.
How often should I rebalance curve positions? Rebalancing frequency depends on strategy type and market conditions, but most curve trades benefit from weekly position reviews with adjustments based on changing curve shapes and risk parameters.
Can I hedge curve positions with spot crypto? Spot hedging can provide some directional protection but doesn’t address curve-specific risks. Using other futures contracts or derivatives typically provides more precise hedging for curve strategies.
How do I calculate potential returns for curve trades? Return calculations must consider premium decay, time horizons, transaction costs, and opportunity costs. Simple premium differences often overstate actual realizable returns.
What’s the relationship between volatility and curve shapes? Higher volatility typically steepens curves as longer-term uncertainty premiums increase, while low volatility periods often coincide with flatter curve structures.
How do I know when to exit curve trades? Exit criteria should be predetermined based on curve normalization levels, time decay, or changes in underlying market conditions that invalidate the original trade thesis.
Can curve trading work during sideways markets? Sideways markets often provide excellent curve trading conditions as time decay and premium convergence work without strong directional interference, making systematic strategies particularly effective.
CryptoPulseHQ is a crypto-focused publication built by professional traders, for traders. With over 6 years of experience in the crypto space, our mission is to simplify exchanges, tools, and strategy - so you can trade smarter and stay one step ahead.
We publish daily guides, comparison blogs, and step-by-step tutorials to help you navigate the fast-moving world of crypto with clarity and confidence.
This guide was written by a cryptocurrency researcher with extensive experience in altcoin platforms, decentralized trading tools, and global exchange analysis. Our goal is to help users trade securely and responsibly through transparent education. -
**Disclaimer:** This content is for informational purposes only and does not constitute financial, investment, or legal advice. Always review the laws in your country before using any cryptocurrency platform. Trading involves risk, and past performance is not a guarantee of future results. Some of the links on this site are affiliate links, which means we may earn a commission if you click through and make a purchase - at no additional cost to you.


